This site is inactive as of February 2020. For updated information on an initiative's work, please refer to their own website as listed in their contact details.
Summary
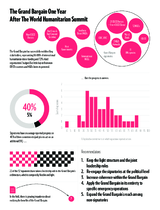
The Grand Bargain is an agreement between some of the largest donors and aid providers, which aims to get more means into the hands of people in need.
The Grand Bargain was first proposed by the former UN Secretary General’s High-Level Panel on Humanitarian Financing in its report “Too Important to Fail: addressing the humanitarian financing gap” as one of the solutions to address the humanitarian financing gap.
The Grand Bargain includes a series of changes in the working practices of donors and aid organisations that would deliver an extra billion dollars over five years for people in need of humanitarian aid. These changes include gearing up cash programming, greater funding for national and local responders and cutting bureaucracy through harmonised reporting requirements.
The Grand Bargain commits donors and aid organizations to providing 25 per cent of global humanitarian funding to local and national responders by 2020, along with more un-earmarked money, and increased multi-year funding to ensure greater predictability and continuity in humanitarian response, among other commitments. Further information can be found in the official website of the Grand Bargain, https://interagencystandingcommittee.org/grand-bargain-hosted-iasc/.
Partners
As of 1 July 2019, the following 61 donors and aid organisations endorse the Grand Bargain:
- ActionAid International
- Australia
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- CAFOD
- Canada
- CARE International
- Catholic Relief Services
- Christian Aid
- Czech Republic
- Danish Church Aid
- Denmark
- Estonia
- European Commission - ECHO
- FAO
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Global Communities
- ICRC
- ICVA
- IFRC
- ILO
- InterAction
- IOM
- IRC
- Ireland
- Italy
- Japan
- Luxembourg
- Médecins du Monde
- Mercy Corps
- Near Network
- New Zealand
- Norway
- NRC
- OCHA
- OECD
- Oxfam
- Relief International
- Save the Children
- SCHR
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syria Relief
- The Netherlands
- UN Women
- UNDP
- UNFPA
- UNHCR
- UNICEF
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
- UNRWA
- WFP
- WHO
- World Bank
- World Vision International
- ZOA International

Goals
To get more means into the hands of people in need and to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of humanitarian action, the Grand Bargain sets out 51 commitments distilled in 9 thematic work streams and one cross cutting commitment:
1. Greater Transparency
2. More support and funding tools to local and national responders
3. Increase the use and coordination of cash-based programming
4. Reduce Duplication and Management costs with periodic functional reviews
5. Improve Joint and Impartial Needs Assessments
6. A Participation Revolution: include people receiving aid in making the decisions which affect their lives
7. Increase collaborative humanitarian multi-year planning and funding
8. Reduce the earmarking of donor contributions
9. Harmonize and simplify reporting requirements
Enhance engagement between humanitarian and development actors
Resources







_0.png)


 summary
summary partners
partners goals
goals Stakeholder reports
Stakeholder reports resources
resources contacts
contacts